Python常用代码片段
# 读写json文件
特别注意编码:
读写文件时建议使用utf8编码,不然中文会乱码
json.dump序列化时默认使用ASCII码,想要在json文件中显示中文,需要指定ensure_ascii=False
import json
# 读取json文件
with open(json_file, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
data = json.load(f)
# 写入json文件
with open(json_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(data, f, ensure_ascii=False)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 逐行读写文本
with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
lines = f.readlines()
for i in range(len(lines)):
do_something()
with open(file_path, "w", encoding='utf8') as f:
content = "".join(lines)
f.write(content)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 读写csv文件
demo.csv
id,name
1,张三
2,Tom
3,Peter
2
3
4
读取csv文件内容:
import csv
with open('demo.csv', 'r', encoding='utf-8')as f:
csv_reader = csv.reader(f)
for row in csv_reader:
print(row)
# output
'''
['id', 'name']
['1', '张三']
['2', 'Tom']
['3', 'Peter']
'''
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
生成csv文件:
- 注意编码encoding='utf-8-sig'
- 如果不写newline='',生成的csv文件中可能会出现很多空行
import csv
data = [
['id', 'name'],
['1', '张三'],
['2', 'Tom'],
['3', 'Peter']
]
# 注意这里编码是utf-8-sig
with open('demo.csv', 'w', encoding='utf-8-sig', newline='') as f:
csv_writer = csv.writer(f)
for row in data:
csv_writer.writerow(row)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 配置文件解析器:configparser
官方文档:configparser --- 配置文件解析器 (opens new window)
它可以解析类似 Microsoft Windows INI 这样的文件。
例如长这样:config.ini
# 这是注释
; 这是注释
[Default]
url = https://baidu.com
name = 张三
[Debug]
isDebug = False
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
使用方法(这是一个有坑的例子,后面才是常用的方法):
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('config.ini')
for section in config.sections():
print(f"Section: {section}")
for key in config[section]:
print(f"Key: {key} Value: {config[section][key]}")
# Output
# Section: Default
# Key: url Value: https://baidu.com
# Key: name Value: 寮犱笁
# Section: Debug
# Key: isdebug Value: False
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
根据上面的例子并且参考官方的解释,有以下几点需要注意:
所有key、value都是以字符串的形式存储,如果需要其它数据类型需要自行转换。
注意读取的时候编码设为
utf-8,不然中文会乱码。默认情况下所有的Key都会被强制转换成小写,想要保持大写参考这里:ConfigParser.optionxform(option) (opens new window)
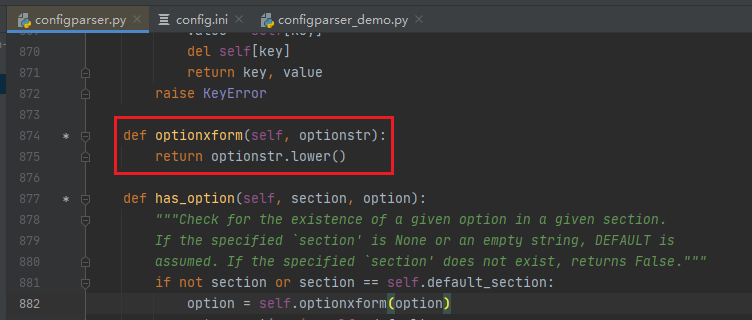
下面是解决了以上问题的例子:
import configparser
config = configparser.RawConfigParser()
# 解决Key默认转小写的问题,直接返回原字符串
config.optionxform = lambda option: option
# 解决中文乱码问题,加上utf-8编码
config.read('config.ini', encoding="utf-8")
for section in config.sections():
print(f"Section: {section}")
for key in config[section]:
print(f"Key: {key} Value: {config[section][key]}")
# Output
# Section: Default
# Key: url Value: https://baidu.com
# Key: name Value: 张三
# Section: Debug
# Key: isDebug Value: False
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 读写YAML文件
例如有config.yaml:
# 这是注释
name: 张三
sex: Male
class: Priest
title: Acolyte
hp: [32, 71]
sp: [1, 13]
gold: 423
inventory:
- a Holy Book of Prayers (Words of Wisdom)
- an Azure Potion of Cure Light Wounds
- a Silver Wand of Wonder
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Python读写yaml文件的方式:
import yaml
from pprint import pprint
# 读取
with open("config.yaml", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
data = yaml.safe_load(f)
pprint(data)
# 写入
with open("test.yaml", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
yaml.safe_dump(data, f, allow_unicode=True)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
输出:
{'class': 'Priest',
'gold': 423,
'hp': [32, 71],
'inventory': ['a Holy Book of Prayers (Words of Wisdom)',
'an Azure Potion of Cure Light Wounds',
'a Silver Wand of Wonder'],
'name': '张三',
'sex': 'Male',
'sp': [1, 13],
'title': 'Acolyte'}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 获取某个文件夹中的所有文件
- os.listdir获取指定目录下第一层的所有文件名列表,包括文件夹和文件
- 生成指定文件的路径用os.path.join,可以避免操作系统路径分隔符不同的问题
import os
folder_path = "./"
# 获取某个文件夹中所有文件列表
file_list = os.listdir(folder_path)
# 区分文件和文件夹
folders = []
files = []
for file in file_list:
file_path = os.path.join(folder_path, file)
if os.path.isdir(file_path):
folders.append(file)
else:
files.append(file)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# logging模块的使用
logging模块 (opens new window)是Python官方的日志记录工具。
格式化可用的属性:LogRecord 属性 (opens new window)
记录一下我常用的格式,已封装成一个模块:fine_logger.py
from logging import *
class FineLogger(Logger):
def __init__(self, name, level=NOTSET):
Logger.__init__(self, name=name, level=level)
def init_log_file(self, log_path="debug.log"):
"""
如果要同时把日志记录到文件中,需要通过此方法设置路径
:param log_path: 日志文件路径
"""
# 使用FileHandler把日志输出到文件
file_handler = FileHandler(log_path, encoding='utf-8')
file_handler.setFormatter(formatter)
self.addHandler(file_handler)
fine_logger = FineLogger("root")
# log级别
fine_logger.setLevel(INFO)
# 设置格式
formatter = Formatter('%(asctime)s thread-%(threadName)s %(module)s [%(levelname)s] %(message)s',
datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
# 使用StreamHandler把日志输出到控制台
stream_handler = StreamHandler()
stream_handler.setFormatter(formatter)
fine_logger.addHandler(stream_handler)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
使用时只需要导入fine_logger模块:app.py
from fine_logger import fine_logger
# 如果要同时把日志记录到文件中,需要先设置日志路径,默认是./debug.log
fine_logger.init_log_file()
fine_logger.info("Hello")
2
3
4
5
6
输出格式如下:
2022-03-22 22:40:56 thread-MainThread app [INFO] Hello
# 使用traceback打印异常信息
捕获异常时如果直接打印str(e)得到的信息很少,而使用traceback可以打印出堆栈信息。
官方文档:traceback --- 打印或检索堆栈回溯 (opens new window)
demo.py
import traceback
try:
a = 1/0
except Exception as e:
print(traceback.format_exc())
2
3
4
5
6
7
output:
注意这里是打印出了异常的堆栈信息,程序并没有异常中断
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "**/demo.py", line 5, in <module>
a = 1/0
ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
2
3
4
# 获取当前时间戳
更多格式可以参考文档:time.strftime(format[, t]) (opens new window)
print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()))
# 2022-03-25 15:48:51
2
# 生成requirements.txt
python -m pip freeze > requirements.txt
# subprocess模块
subprocess是Python标准库中的一个模块,用于在Python程序中创建子进程并与其交互。
subprocess模块提供了多个函数和类,可以方便地执行外部命令,获取命令的输出和错误信息,以及向命令传递输入。其中比较常用的函数包括:
- subprocess.run(): 执行外部命令并等待其完成,返回一个CompletedProcess对象,包括命令的退出状态码、标准输出、标准错误等信息。
- subprocess.call(): 执行外部命令并等待其完成,返回命令的退出状态码。
- subprocess.check_call(): 执行外部命令并等待其完成,如果命令的退出状态码不为0则抛出异常。
- subprocess.check_output(): 执行外部命令并等待其完成,返回命令的标准输出。
- subprocess.Popen(): 执行外部命令,返回一个Popen对象,可以通过该对象的方法和属性与子进程交互,例如向其输入数据、发送信号等。
subprocess模块的使用可以避免在Python程序中使用os.system()和os.popen()等函数执行外部命令,能够更加方便地获取命令的输出和错误信息,并且具有更好的跨平台性。
import subprocess
def execute_command(command):
"""
执行一条shell命令
"""
print(f"Execute Command: {command}")
result = subprocess.run(args=command, shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
print(f"stdout:\n{result.stdout.decode('utf-8')}")
if result.returncode != 0:
raise Exception(f"stderr:\n{result.stderr.decode('utf-8')}")
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
注意:
shell=True:意为通过 shell 来执行命令,此时可以把命令和参数写在一个字符串中,如果使用默认值false,则命令和参数必须分开写。